
Oral Ulceration
Contents
ToggleOral Ulceration
Objectives
By the end of these revision notes, you should:
What are ulcers?
Oral ulceration may be primary (occurring on their own) or secondary (occurring as vesicles first then turning in to ulcers).
Ulcers represent a break in the epithelium, which exposed the underlying connective tissue. The full thickness of the epithelium is typically replaced by a fibrinous slough, with. a mix of inflammatory cells.
Causes of ulcers
There are many causes of ulcers, which all present with different histories and have different methods of management. Oral ulceration may occur as a single or multiple episodes and may present as a single lesion or multiple lesions. Causes of oral ulceration include:
- Trauma
- Malignancies
- Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS)
- Gastrointestinal disorders
- Anaemia
- Drug-induced
- Irradation
- Herpes infections
- Vesicular bullous disorders
- Lichen planus
- Erythema multiforme
- Behçets disease
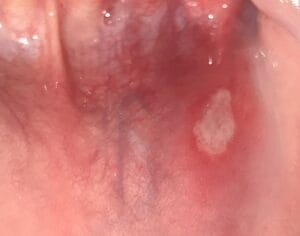
Taking an oral ulceration history

🚨 Access Restricted

Subscribe to access ALL revision notes and cheat sheets!
We provide a wide range of revision notes and cheat sheets to help you study and prepare for exams! To access all we have to offer, head over and subscribe to ExamineDental now to supercharge your revision!
